The next generation of wireless communications could be just around the corner, but a leading engineer says most of us will never be able to use it.
Eddie Ball, a radio engineering expert at the University of Sheffield, believes 6G networks could be available as early as 2030.
This new technology will allow downloads that previously took a few seconds with 5G to be completed in just milliseconds.
However, Hall warns that 6G technology will be so powerful that it will likely drain a phone’s battery in just 30 minutes.
Mr Ball says: ‘A major issue is the energy efficiency of the radio systems needed to deliver high data rates in the future, which will result in shorter battery lives for mobile devices.’
An expert engineer says 6G could arrive by 2030, but warns it will be so demanding it will drain your phone’s battery in just 30 minutes (file image)
6G, or sixth generation wireless technology, is the next stage in the evolution of wireless technology.
Although 5G technology only began to be rolled out in the UK in 2019, its successor, 6G, could be more than 100 times faster and could support communications with microsecond latency.
Speaking ahead of the British Science Festival in London this week, Mr Ball said: “If you’re on 5G it seems quite fast when you’re using your phone, but with 6G it’s almost instantaneous, no delays at all.”
Researchers have yet to determine exactly how fast 6G will be, but some estimates suggest it could theoretically transfer 1TB of data per second.
This makes it ideal for applications such as remote surgery or autonomous cars that require extremely fast reactions.

6G is the next generation of wireless mobile networks and will allow downloads to be completed in just milliseconds (stock image)
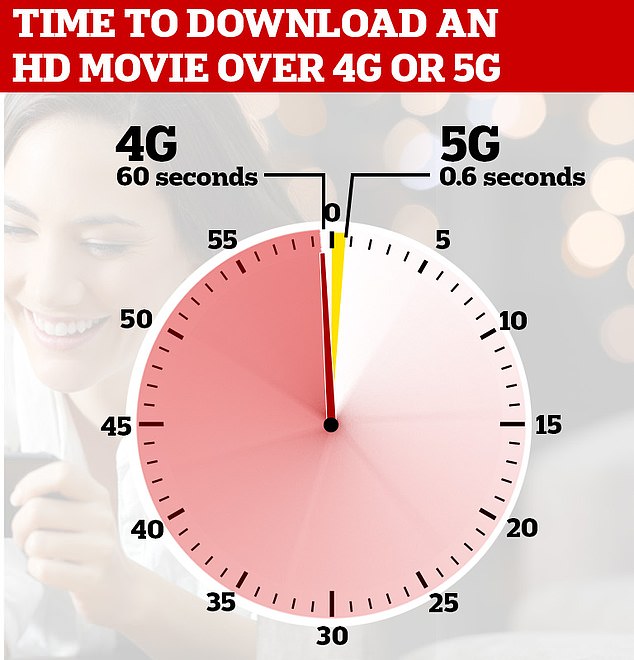
As this chart shows, 5G technology is up to 1,000 times faster than older 4G networks. The next generation of 6G is expected to be up to 100 times faster.
Mr Ball is currently showcasing his research into technologies that could make 6G possible at the University of East London’s British Science Festival.
He believes this next-generation technology will soon enable ultra-fast internet speeds.
However, the vast majority of people will not be able to directly benefit from this advancement.
Transferring data in such large volumes requires a huge amount of energy, a problem that is compounded by the fact that current 6G hardware is extremely energy inefficient.
If a modern smartphone were equipped with 6G technology, simply transferring data over the network would completely drain its battery in just 30 minutes.
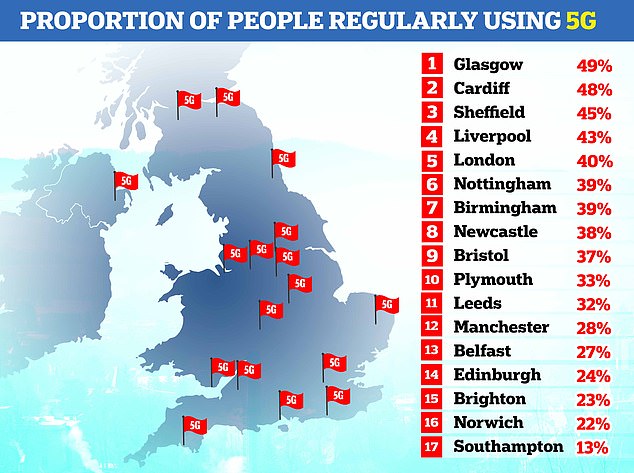
Research from 2022 found that many people in Britain were yet to feel the benefits of 5G networks. Experts believe it will take even longer for 6G to become mainstream
“Our research at the University of Sheffield has begun to identify new techniques and architectures that can deliver improved energy efficiency and performance, but we are still years away from seeing that become a reality in our everyday lives,” Ball said.
Additionally, since 6G is a completely new technology, current telephone and national infrastructure will need to be upgraded, just as the transition to 5G required the installation of new towers.
Mr Ball said: ‘6G technology will only be successful if we have new advanced radio frequency systems to deliver it.
‘The UK’s current infrastructure, including hardware, mobile phones and antennas, is not fit for purpose.’
Since the necessary infrastructure upgrade would be so expensive, it is likely to be installed only in areas that require extremely large data transfers.
These areas could include data centers and artificial intelligence research facilities, highways used by autonomous vehicles, or so-called “drone superhighways.”

Just as 5G required the installation of new transmitters (pictured), 6G networks will require expensive infrastructure upgrades that will only be practical where extremely large data transfers are needed.
This means that even if your phone was able to connect to 6G, the coverage would be so spotty that it would fall back to 5G most of the time.
For this reason, mobile phones are not likely to be upgraded to a 6G network in the near future.
While the creation of 6G will be a major breakthrough, Ball said those developing the technology are still not quite sure what to do with it and described it as a solution in search of a problem.
“Operators are trying to define a decisive use case for 6G, but I would say that it remains to be seen what that is,” he added.
One possibility is for doctors to use very small, short-range 6G networks to remotely operate surgical robots.
This would produce extremely low latencies and high fidelity needed to perform the most delicate operations.
However, Mr Ball also cannot rule out researchers soon discovering “all sorts of weird, weird and wonderful applications that we can really only guess at what they might be”.

