<!–
<!–
<!– <!–
<!–
<!–
<!–
According to a new study, artificial intelligence has discovered two plants that provide the same weight loss results as Ozempic.
Researchers from the Catholic University of Murcia in Spain reported that the plants contain similar agonists (a substance that mimics a hormonal response) to those in Ozempic.
The artificial intelligence software analyzed thousands of natural compounds that could offer the same weight loss components and ultimately narrowed down two plant extracts.
Researchers set out to find a plant-based alternative because many people experience side effects and regain weight once they take the prescription medication.
The team also said that plants would not only be gentler on the body, but would also be more accessible and cost-effective: Ozempic costs about $936 a month.
They won’t name the plant extracts, which for now have been called Compound A and Compound B, until they patent them for a new weight-loss drug.
Ozempic’s maker, Novo Nordisk, is preparing to launch a new drug, amicretin. Early results from the drug’s safety trial suggest it may help users lose weight twice as fast as Ozempic.
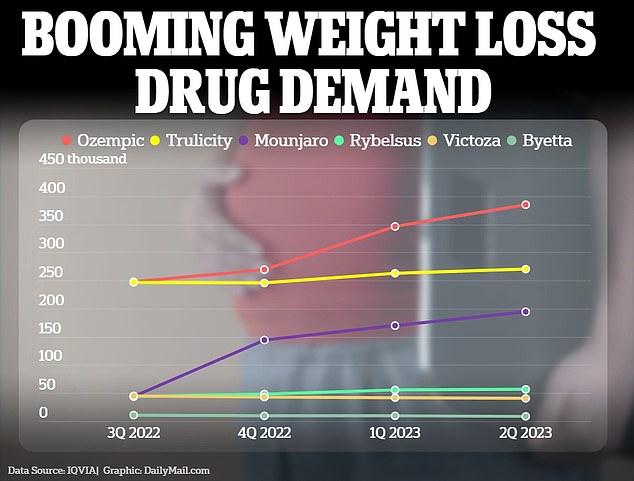

Weight loss medications increased last year, with Ozempic leading the way as the most used option
Ozempic was launched in 2017 to treat people with diabetes, but was later discovered to help people lose weight by suppressing appetite.
Since it was heralded as a “miracle drug,” its use has increased 300 percent in less than three years, with prescriptions reaching nine million in the US as of September 2023.
Morgan Stanley analysts have projected that in the next 10 years, 24 million people (seven percent of the US population) will take Ozempic or Wegovy.
But users have reported episodes of nausea and vomiting, as well as mental health problems such as anxiety and irritability when receiving the weekly injections.
To address these issues, the scientists wanted to “focus on plant extracts and other natural compounds because they may have fewer side effects” and options that could be taken orally instead of as an injection.
But the necessary alternative to still activates the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) receptor, which is like Ozempic triggers body weight loss answer.
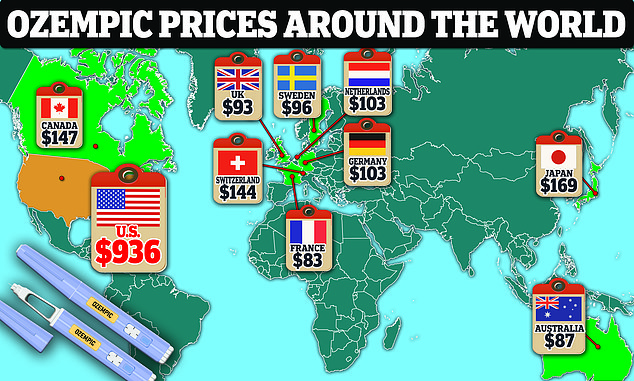

Ozempic can cost up to $935 per month before health insurance, while the cost abroad is around $100 on average.
“Non-peptide drugs may have fewer side effects and be easier to administer, meaning they could be given in pill form rather than injections,” said Elena Murcia, co-author of the study and member of the Structural and Bioinformatics Group. Alta -Performance Computing Research Group (BIO-HPC).
The team used AI-powered software to screen more than 10,000 compounds and identify those that bound to the GLP-1 receptor.
Other AI-based methods then investigated how closely these bonds resembled those between the hormone GLP-1 and its receptor.
The team identified 100 of the group for visual analysis, which produced a set of 65 compounds that were subjected to a mathematical graph to identify those with the greatest potential as GLP1-R agonists.
And that’s when the team landed on Compound A and Compound B.
The study noted that researchers will not reveal the name of the plants until they have patented them for a new weight-loss drug.
The compounds come from very common plants, according to the report, whose “extracts have been associated in the past with beneficial effects on human metabolism.”
‘Computer-based studies like ours have key advantages, such as reductions in cost and time, rapid analysis of large data sets, flexibility in experimental design, and the ability to identify and mitigate any ethical and safety risks before perform experiments in the laboratory. “Murcia said.
“These simulations also allow us to leverage AI resources to analyze complex problems, providing valuable initial insight in the search for new drugs.”
