Experts warn that a cluster of heart diseases affecting one in three Americans could be fueling a wave of dementia cases across the United States.
Experts at the American Heart Association said coronary artery disease, heart failure and atrial fibrillation prevent blood from flowing properly to the brain, leading to the death of brain cells and tissues.
With more than 130 million Americans suffering from some form of heart disease, experts said preventing it early through diet and exercise could be key to stopping dementia, which affects more than 7 million Americans each year.
Experts from the American Heart Association warned that coronary artery disease, heart failure and atrial fibrillation increase the risk of dementia
Dr. Fernando Testai, a professor of neurology and rehabilitation at the University of Illinois who worked on the statement, said, “Dementia is commonly viewed as an incurable and relentless disease that cannot be prevented.”
“However, evidence shows that adopting a healthy lifestyle and identifying and treating vascular risk factors early can help preserve normal brain function and reduce the burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other related dementias.”
In an article published Thursday in the magazine StrokeExperts for the first time named coronary artery disease as the culprit behind dementia.
Coronary artery disease is the most common heart condition in the US and the leading cause of death, accounting for one in four deaths in the United States each year.
This occurs when plaque from excess cholesterol and fat builds up in the arteries, causing them to narrow.
Over time, this reduces blood flow to the heart, as well as other organs such as the brain.
That reduction in blood flow damages the small blood vessels in the brain, depriving it of vital nutrients needed to maintain cognitive functions.
Experts estimated that coronary artery disease increases the risk of dementia by 27 percent compared to those without heart disease.
They also pointed to heart failure, which affects 6 million Americans and occurs when the heart becomes too weak to pump enough blood.
They suggested that up to eight in 10 people with heart failure could have some type of cognitive impairment, including dementia, that affects their memory, language or ability to think or plan.
Dr. Testai he told CNN that conditions that lead to heart failure, such as diabetes and coronary artery disease, “can increase levels of beta-amyloid in the brain, (a protein) recognized as a key marker of Alzheimer’s disease.”
The third condition that experts pointed out was atrial fibrillation, also known as AF. The condition suffered by celebrities like the president joe biden and miley ciroIt causes an irregular heartbeat that patients have described as a “flutter” in the chest.
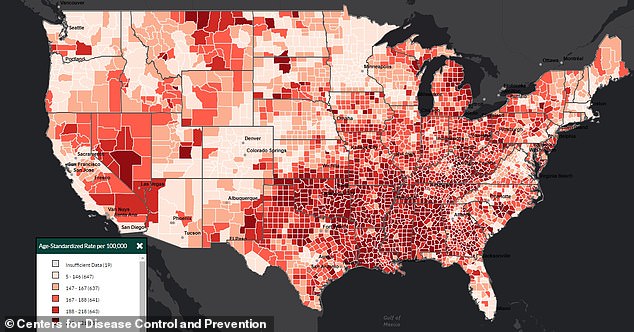
The above shows the heart disease death rate by county in the United States from 2018 to 2020.
Rates of this condition, which affects between 3 and 6 million Americans at any given time, are increasing. Experts estimate that by 2050, up to 16 million Americans will have AF.
The team noted that AF could be linked to dementia through brain microbleeds, or small brain bleeds, which could lead to a stroke.
They estimated that people with FA have a 39 percent higher risk of having memory or thinking problems compared to those without the condition.
Dr. Andrew Freeman, director of cardiovascular prevention and wellness at National Jewish Health in Denver, he told CNN: ‘This call to action is especially critical right now because many Americans have some form of heart disease and people are getting sicker at a younger age.’
The doctor, who was not involved in the article, also said that adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle should start early in life, even before the baby is born.
This includes focusing on anti-inflammatory nutrients popularized by the Mediterranean diet, including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and olive oil.
Additionally, the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend that adults get 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
This could also reduce the risk of dementia. TO study 2022For example, he found that people who walked briskly for 30 minutes a day reduced their risk of dementia by 62 percent.
Dr Freeman said: “Physical activity is absolutely great.
‘And if you combine that with a more plant-based diet, de-stressing, getting enough sleep and connecting with others, that’s your magic recipe.’ It’s the fountain of youth, so to speak.

