Experts have warned against a disease lurking in backyards across the United States after a series of deaths in Australia.
Melioidosis is a serious bacterial lung infection that kills up to half of the people it infects worldwide.
The disease, which affects a dozen Americans a year, is caused by the bacteria Burkholderia pseudomallei, which lives in tropical soils and water.
Experts have suggested that wet weather such as hurricanes and heavy rain, which have become increasingly common in the US, may increase the risk of bacteria rising to the soil surface in gardens and backyards. .
It comes after five people in Australia’s Northern Territory died from the disease, prompting health officials there to issue an alert to the public.
While it is primarily found in tropical climates such as Southeast Asia and Australia, it can spread to certain coastal areas of the U.S. These include the Mississippi Gulf Coast, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria usually causes no symptoms, but in severe cases, it can trigger life-threatening pneumonia and sepsis, the body’s overreaction to an infection that causes the immune system to attack healthy organs.
Last year, CDC officials warned that Burkholderia pseudomallei is now endemic to the Gulf Coast, which includes Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Florida.
Authorities have warned against the melioidosis infection, which is spread by bacteria lurking in gardens and has killed five Australians in the past 12 months (file image)
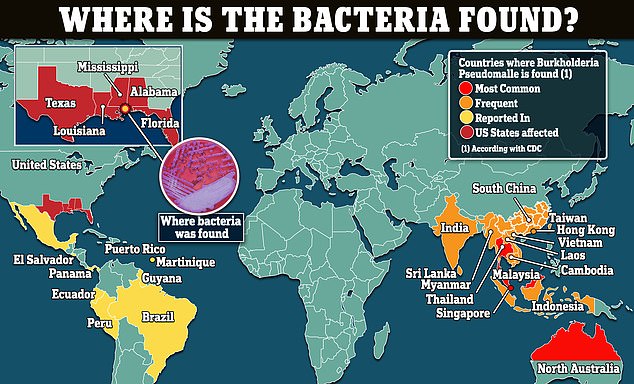
The map above shows the countries where the bacteria has been detected and the US states where the CDC says it is endemic.
Professor Bart Currie, an expert in tropical and emerging infectious diseases at Australia’s Menzies School of Health Research, said Yahoo News Melioidosis will become an “even more important problem in the coming years” due to climate change leading to more hurricanes and monsoons.
Humans can become infected with the bacteria through contact with contaminated soil and muddy water, especially if they have an open wound.
In rare cases, it can also be transmitted between humans, although this has only been reported through sexual contact and during pregnancy.
Burkholderia pseudomallei was first detected in the US in 2022 in soil and water samples along the Mississippi Gulf Coast.
Until then, cases of melioidosis in the United States had been linked to people bringing it from areas such as Australia.
Symptoms include fever, headache, difficulty breathing, stomach or chest pain, muscle pain, confusion, and seizures, according to the CDC.
Signs usually develop one to four weeks after exposure to the bacteria, although some people do not get sick until months or years after exposure.
Although melioidosis usually appears as a lung infection, it can spread to other organs such as the liver, spleen, prostate, lymph nodes, and brain.
In severe cases, it can lead to life-threatening sepsis.
Melioidosis is usually treated with long-term antibiotics, including intravenous antibiotics for at least two weeks (the intensive phase) and oral medications for three to six months (the eradication phase).
To prevent exposure to Burkholderia pseudomallei, the CDC recommends avoiding soil or water if you have open bottoms and wearing gloves and boots when gardening.


