- Dicamba concentrations detected in urine have increased in the last decade
- The herbicide has been linked to liver and bile duct cancer.
- READ MORE: Four in Five Americans Test Positive for Little-Known Toxic Chemical
Pregnant women in areas where agriculture is a large industry may be at risk of being exposed to a chemical that has been linked to cancer.
TO study published in Agrochemicals found that the percentage of pregnant women testing positive for dicamba, a chemical herbicide, increased from 28 percent between 2010 and 2012 to 70 percent between 2020 and 2022.
Researchers from Indiana, Washington and Quebec analyzed the urine of 61 pregnant women in Indiana, one of the largest U.S. agricultural producers of mint, soybeans and corn.
The results also showed that the concentration of the chemical increased from 0.066 micrograms of dicamba per liter of urine to 0.271 micrograms of dicamba per liter of urine.
Dicamba is typically sprayed on crops, including soybeans, and the Environmental Protection Agency has previously acknowledged that the substance can evaporate and spread through the air as a vapor.
The study authors said their findings highlight the need to track herbicide exposure and monitor adverse maternal and neonatal side effects.
The results come at a time when there is an increase in the use and reliance on herbicides and pesticides in agriculture, prompting experts to “sound the alarm.”
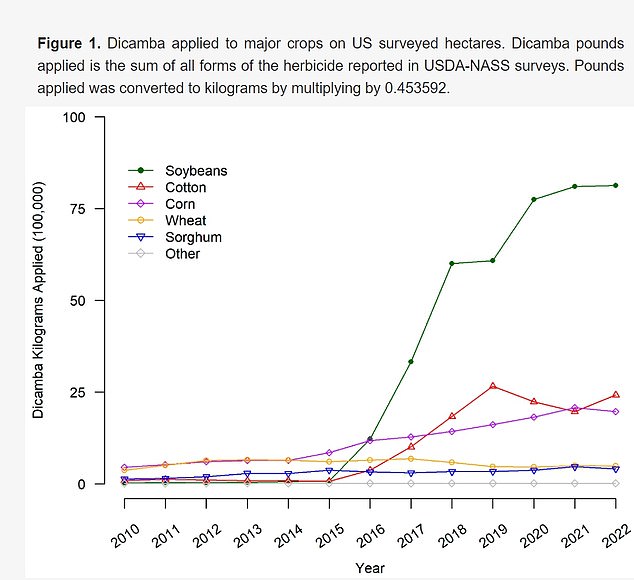
Although dicamba is sprayed on crops, the U.S. Department of Agriculture has found that residues of the chemical are minimal in food.
Therefore, the USDA said people are more likely to be exposed to the chemical through inhalation and contaminated drinking water.
A 2020 study It found that dicamba is associated with an increased risk of liver and bile duct cancer, but more research is needed to understand the full effects.
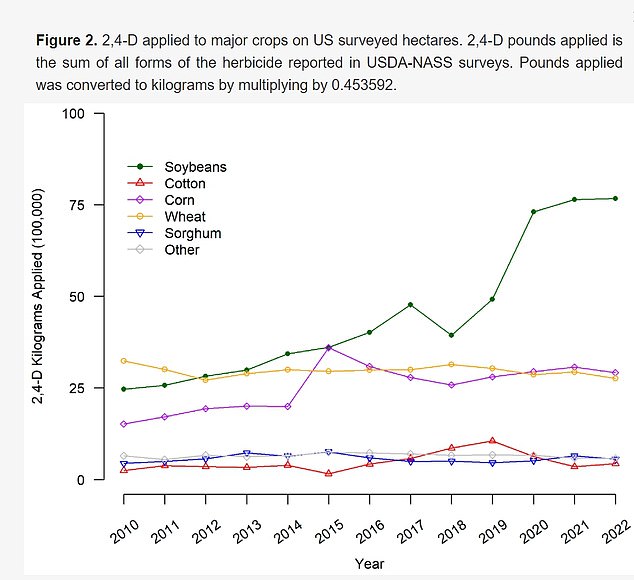
The study also looked at the presence of another chemical in the women’s urine, 2,4-dichloroacetic acid, better known as 2,4-D.
This chemical is also a common herbicide.
While it was detected in 100 percent of the women’s urine, the results showed detectable, but non-significant, increases in concentration levels from 2010 to 2012.
The effects of 2,4-D in the body are less known, but in animals studies have shown that exposure to it during pregnancy is associated with lower body weight and changes in offspring behavior.
Other investigation It has been shown that there is a greater relationship with lymphoma and prolonged exposure can cause kidney and liver damage.
The researchers stated in their study that dependence on herbicides has increased dramatically in the last decade.
Paul Winchester, a professor of pediatrics at Indiana University School of Medicine, who was not involved in the study, said The Guardian: “These are two chemicals we are concerned about due to their increasing use.”
A similar recent study found that four in five Americans tested positive for another agricultural chemical used as a pesticide: chlormequat.
That study found that 80 percent of people tested positive for the substance, which has been linked to reduced fertility, altered fetal development and early onset of puberty.
The results come as there is an increase in the use and reliance on herbicides and pesticides in agriculture, prompting experts to “sound the alarm” due to the detrimental effects these chemicals have been associated with.


