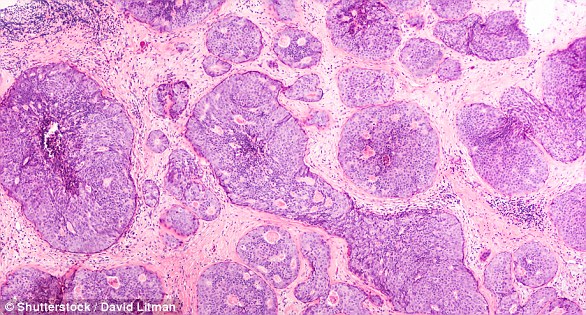
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. Every year in the UK there are more than 55,000 new cases and the disease claims the lives of 11,500 women. In the United States, it strikes 266,000 people each year and kills 40,000. But what is the cause and how to treat it?
What is breast cancer?
It comes from a cancer cell that grows in the lining of a duct or lobule of one of the breasts.
When breast cancer has spread to surrounding tissues, it is called “invasive” cancer. Some people are diagnosed with “carcinoma in situ,” in which no cancer cells have grown beyond the duct or lobule.
Most cases occur in people over the age of 50, but younger women are sometimes affected. Breast cancer can develop in men, although this is rare.
Staging indicates how big the cancer is and whether it has spread. Stage 1 is the earliest stage and stage 4 means the cancer has spread to another part of the body.
Cancer cells are graded from low, meaning slow growing, to high, meaning fast growing. High-grade cancers are more likely to come back after being treated for the first time.
What are the causes of breast cancer?
A cancerous tumor arises from an abnormal cell. Exactly why a cell becomes cancerous is unclear. Something is thought to damage or change certain genes in the cell. This causes the cell to become abnormal and multiply in an “uncontrolled” manner.
Although breast cancer can develop for no apparent reason, certain risk factors can increase the risk, such as genetics.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
The usual first symptom is a painless lump in the breast, although most are not cancerous and are fluid-filled cysts, which are benign.
The first place breast cancer usually spreads is to the lymph nodes in the armpit. If this happens, you will develop a swelling or lump in your armpit.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
- Initial assessment: A doctor examines the breasts and armpits. They may perform tests such as a mammogram, a special X-ray of breast tissue that can indicate the possibility of tumors.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of tissue from a part of the body. The sample is then examined under a microscope to look for abnormal cells. The sample can confirm or rule out cancer.
If you are confirmed to have breast cancer, additional tests may be needed to assess whether the cancer has spread. For example, blood tests, liver ultrasound or chest x-ray.
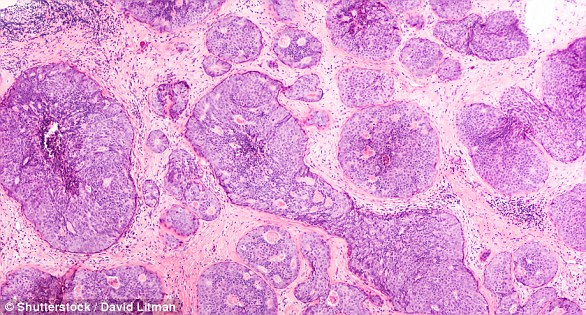
How is breast cancer treated?
Treatment options that may be considered include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal treatment. Often a combination of two or more of these treatments is used.
- Surgery: Breast-conserving surgery or removal of the affected breast depending on the size of the tumor.
- Radiotherapy: treatment that uses high-energy beams of radiation focused on cancerous tissue. This kills cancer cells or stops them from multiplying. It is mainly used as an adjunct to surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Treatment of cancer using anticancer drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Hormonal treatments: Some types of breast cancer are affected by estrogen, a “female” hormone, which can stimulate cancer cells to divide and multiply. Treatments that reduce the level of these hormones, or stop them from working, are commonly used in people with breast cancer.
How successful is the treatment?
The outlook is best in those who are diagnosed while the cancer is still small and has not spread. Surgical removal of a tumor at an early stage can then give a good chance of cure.
With routine mammography available to women aged 50 to 70, more breast cancers are being diagnosed and treated at an early stage.
For more information, visit breastcancernow.org or call its free helpline on 0808 800 6000.