Experts warn of overlooked food groups that protect against cancer following a major study.
They are encouraging people to eat more fiber, which is found in foods like oatmeal, beans and popcorn, and calcium, which is found in yogurt, cow’s milk and sardines.
The new study found that a diet low in vegetables, fiber and calcium was responsible for 35 percent of colon cancers.
Researchers analyzed federal health data on more than 700,000 U.S. cancer cases and known risk factors such as smoking, radiation, obesity and diet.
Although smoking was the most common risk factor for all forms of cancer, diet was linked to one in 20 cases overall.
American Cancer Society researchers found that diets low in fiber but high in processed meats may increase the risk of colorectal cancer
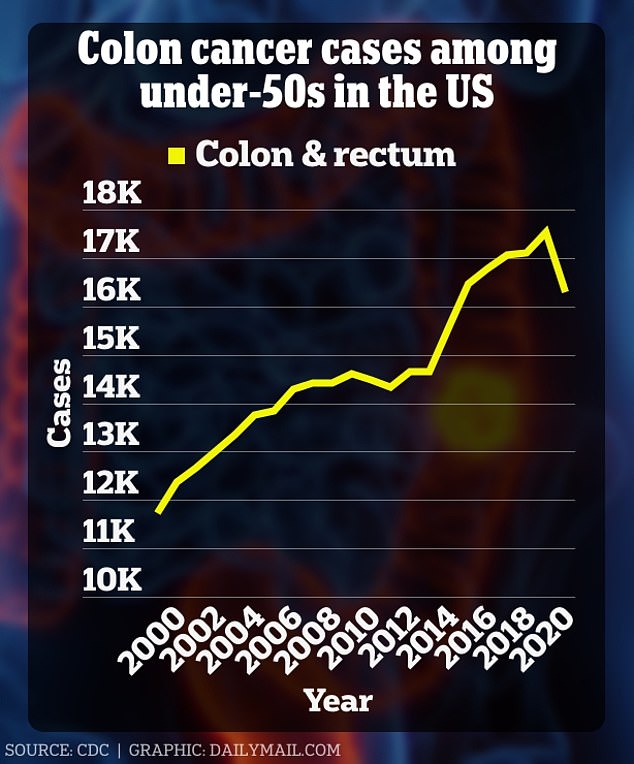
The chart above shows that colon cancer cases among those under 50 rose by more than 5,500 in 20 years. There is a drop in 2020 because the Covid pandemic caused fewer people to come forward for screening.
These dietary factors included a lack of calcium, which helps maintain healthy bones, muscles and the heart, among other functions.
Experts believe it also helps bind fatty acids in the colon to prevent the formation of colorectal cancer cells.
Health agencies recommend between 1,000 and 2,500 milligrams per day from sources such as rye bread, broccoli, milk and yogurt.
In addition, a lack of fiber could cause colorectal cancer in 12 percent of cases, since it helps maintain necessary digestive functions and eliminate carcinogens from the colon.
TO Recent analysis They found that 95 percent of Americans don’t get enough fiber, which can be found in whole grains like oatmeal and fruits like strawberries.
Meanwhile, men who don’t eat enough fruit and vegetables could be 30 percent more likely to develop throat cancer, and nearly nine in 10 cases could be prevented with a healthy diet.
The study, published last month by the American Cancer Society (ACS) They found that overall, diet was associated with only four percent of cancer cases and deaths.
However, unhealthy diets had the strongest association with colorectal cancer.
They found that about 13 percent of colorectal cancers could be attributed to processed meats such as sausages, bacon and hot dogs, a percentage that rises to 14.6 percent in men.
The ACS team found that just over half of colorectal cancers could be prevented with lifestyle changes, and 35 percent were related to diet.
It is still unclear why these meats may contribute to colorectal cancers, but other recent studies have put forward theories.

Increasing intake of folate-rich foods, such as kale and spinach, may reduce the risk of oral and throat cancer in men
A study led by researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, for example, found that compounds linked to processed meats, called metabolites, are at higher levels in younger people with colorectal cancer than in those over age 50.
The lead researcher on that study, Dr Suneel Kamath, previously told DailyMail.com that the metabolites likely help feed cancer cells and “hijack” normal cells. This causes tumors to grow while depriving healthy cells of the energy needed to maintain their normal functions.
However, it remains to be seen why the levels of these metabolites are lower in younger people than in older people with the same disease.
Fiber is essential for several digestive functions, including bulking up stool so it passes more easily and preventing cancer-causing chemicals from remaining in the colon and rectum.
Research from Ohio State University also suggests that diets low in fiber and high in sugar may “accelerate the aging” of cells, leaving them more vulnerable to cancer.
Fruits such as pears, strawberries and avocados, as well as whole grains such as oats, have the highest fiber content.
Additionally, not eating enough calcium-rich foods, such as milk, yogurt and sardines, was linked to about 4 percent of colorectal cancers, the ACS researchers found.
It’s not clear exactly how calcium may reduce the risk of colorectal cancer, although previous studies suggest it helps bind fatty acids in the colon that inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
Additionally, calcium can help form calcium-phosphate-bile acid complexes, which help the colon digest fat.
The ACS study also found that low fruit and vegetable consumption contributed to one in three cancers of the oral cavity, esophagus, pharynx and larynx, as well as 31 percent of deaths.
This could be because eating fruits and vegetables has been shown to reduce the risk of contracting human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection that is the main cause of cervical cancer in women and throat and mouth cancer in men.
According to Moffitt Cancer Center in Florida, fruits and vegetables with folate are the most likely to reduce the risk of contracting HPV. These include spinach, kale, eggs and citrus fruits such as oranges.
The ACS team also found that up to nine out of 10 oral and throat cancers could be prevented with healthier lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking and exercising.


