Anti-Covid vaccines have been linked to small increases in heart, blood and neurological disorders, according to the largest global study of its kind.
An international coalition of vaccine experts looked for 13 medical conditions among 99 million people who received the vaccine in eight countries to identify higher rates of those conditions after receiving the shots.
They confirmed that shots made by Pfizer, Moderna and AstraZeneca are linked to a significantly increased risk of five medical conditions, including a nerve-wearing condition that leaves people with difficulty walking or thinking.
But the study also warned of several other disorders that they said warranted further investigation, including links between a brain inflammation condition and the Moderna shot.
Still, the team says the absolute risk of developing any of these conditions remains small. For example, 13 billion doses of vaccines have been administered and there have only been 2,000 cases of all diseases.
Researchers identified 12 conditions that could be linked to various Covid vaccines. Among the most concerning are inflammation of the heart muscle and inflammation of the brain.
The injections were linked to a variety of diseases, but the risk was still relatively small.
Dr. Harlan Krumholz, director of the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation at Yale New Haven Hospital and principal investigator of the study, said, “Both of these things may be true.”
“They can save millions of lives and there may be a small number of people who have been negatively affected.”
It is estimated that Covid vaccines have prevented more than 19 million deaths worldwide, including three million in the United States alone.
Among their discoveries was a twofold increase in the risk of a neurological condition known as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the body’s peripheral nervous system, damaging the protective covering that surrounds cells. nervous
The report said that of the 23 million AstraZeneca shots administered worldwide, 76 cases of GBS would have been expected, but 190 events were observed, representing a 2.9 times higher risk.
While it cannot be proven that the vaccine caused these events, there is some evidence that the vaccine causes the immune system to attack its own nerves.
Meanwhile, the study also confirmed a three-fold increased risk of a type of heart inflammation called myocarditis, although the researchers did not provide the number of expected cases compared to actual cases.
Myocarditis was seen more frequently in young men. It is believed to be related to the immune response triggered by the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, which work by directing cells to produce the same protein found on top of the coronavirus.
This causes the immune system to produce antibodies against the spike protein, providing protection against Covid. In rare cases, this immune response can cause inflammation in the heart muscle.
Cases of myocarditis have generally been relatively mild, causing only 28 deaths.
Additionally, both the first and fourth doses of the Moderna vaccine had between 1.7 and 2.6 times more cases of pericarditis, an inflammation that affects the protective sac that lines the heart.
They examined more than 39 million doses of the Moderna vaccine administered.
Like the link between mycarditis and vaccines, links to pericarditis are still under investigation. It is thought to be caused by the same mechanism, an overactive immune response that attacks the thin sac-like membrane.
There was a 3.7-fold increased risk of developing a condition called acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), which causes inflammation in the brain and spinal cord that damages the protective covering of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, after the first dose of Moderna. vaccine.
Seven cases of ADEM occurred following vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, exceeding the expected case count of two.
Nearly 190 million injections were considered in the study.
The study also found that after receiving the first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine, there were 1.9 and 3.9 times increased risks of transverse myelitis and ADEM, respectively.
Bell’s palsy, which causes temporary weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face, had an increased odds of 1.05 after a first dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
There was also a 1.3 to 1.4 times higher risk of having a seizure after the first and second doses of the Moderna vaccine, as well as the fourth dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
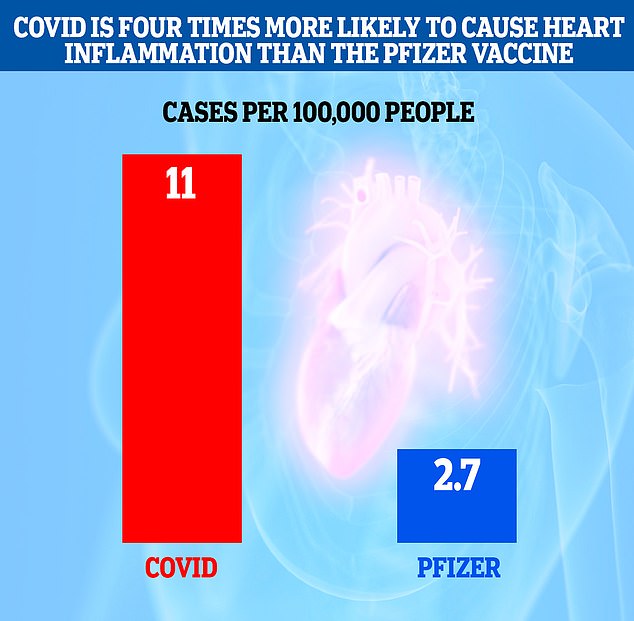
Researchers in Israel detected 2.7 additional cases of myocarditis per 100,000 people injected with the Pfizer vaccine, but this shot up to 11 additional cases per 100,000 people who contracted the virus.
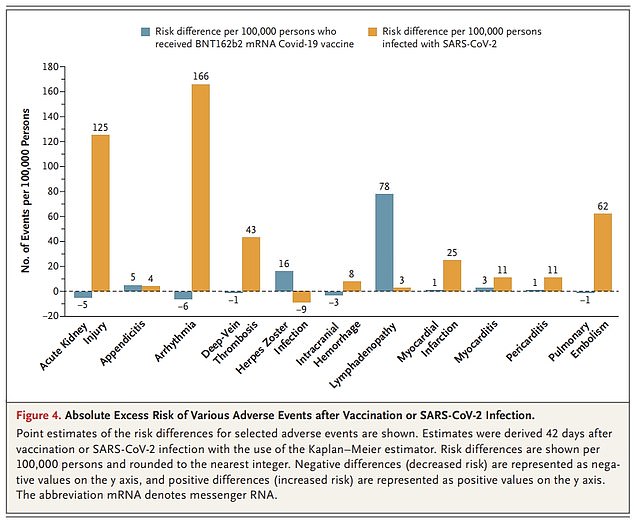
The graph shows the number of additional cases of each adverse effect per 100,000 people after a Pfizer injection (gray bars) and a Covid infection (orange bars).
The researchers added an important caveat to this finding: “The chances of suffering a neurological event after an acute SARS-CoV-2 infection were up to 617 times higher than after COVID vaccination, suggesting that the benefits of vaccination substantially outweighs the risks.
After a first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine, there was a 3.2 times higher than expected risk of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST).
The risks after the first dose of the Pfizer vaccine and after the second dose were 1.49 and 1.25 times higher.
CVST is a rare but serious condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the large channels that drain blood from the brain and return it to the heart after the AstraZeneca vaccine.
In total, 21 events were expected, while 69 events were observed.
Also after the first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine, there was a 1.07 times increased risk of thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by a lower than normal number of platelets in the blood.
After a third dose of ChAdOx1, the risk increased markedly to 1.95.
Their research was published in the journal. Vaccine.