by Mia de Graaf, US Health Editor
Stents keep arteries open to help improve blood flow to the heart and relieve chest pain.
former president of the American Heart AssociationDr. Sidney Smith, MD, told DailyMail.com how stents work and when they are placed.
HOW IS THE PROCEDURE CARRIED OUT?
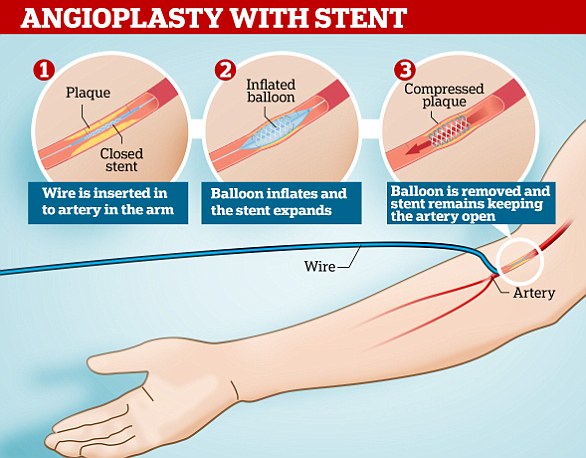
A stent is a wire mesh tube that keeps your arteries open.
To open the narrowed artery, the surgeon may perform what is known as angioplasty.
It involves making a small incision in the patient’s arm or leg, through which a wire with a deflated balloon attached is passed to the coronary arteries.
In some cases, this is all that is needed to break up the blockage, without needing to place any permanent artery opener.
However, sometimes surgeons place a stent to keep the arteries open.
The stent surrounds the balloon and expands with it when it is inflated.
Once the balloon is deflated and removed, the stent remains in the artery permanently.
A stent is a wire mesh tube used to keep an artery open during angioplasty. Once the balloon is removed, the stent remains to keep the artery open.
HOW COMMON IS IT?
Angioplasties are becoming more common in the United States and Mexico due to rising rates of heart problems.
And stents are becoming more common in angioplasty patients, as it is very common for the arteries to narrow again if nothing is placed (this is known as restenosis and occurs in about a third of cases).
CAN IT BE DONE DAYS OR WEEKS AFTER A HEART ATTACK?
Yes, depending on the type of heart attack suffered.
There are two types of locks: a STEMI (which is a complete lock) and a NSTEMI (a partial lock).
STEMI stands for “ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction,” which means that the patient has suffered changes in cardiac enzymes and changes in the electrical activity of the heart, as seen on an electrocardiogram.
A non-STEMI heart attack or a NSTEMI heart attack is less urgent. It means they suffered enzymatic changes but no change in their EKG.
“A STEMI is a very large, serious heart attack where a patient comes to the emergency room and the artery is completely blocked and they need to be opened immediately and the stent placed,” said Dr. Smith, professor of Medicine and Cardiology. University of North Carolina School of Medicine, explained.
“That’s the patient who goes straight to surgery.”
‘In other cases, the patient may have a STEMI. They may have chest pain and arrive at the hospital with changes in enzymes, but no changes in their ECG (electrical activity of the heart). The need is not urgent. Stents are placed but it may be days later.’
WHY DOES A PATIENT GET MORE THAN ONE STENT AT A TIME?
It depends on how many blockages they had or how many vessels were affected.
“The decision to stent the coronary arteries is based on the number of major blockages that exist,” Dr. Smith explained.
‘Three is not something out of the ordinary. Sometimes you place just one, sometimes two or three; It depends completely.
‘Stents are placed where there is significant obstruction. It could be that there were two or three vessels involved, or three blockages on one vessel. That would justify three stents.
He adds that the number of blockages has nothing to do with the severity of the heart attack, or whether it would be a STEMI or NSTEMI.
WHAT IS RECOVERY LIKE?
For patients treated for chest pain, most are usually able to go home the same day as the operation. Patients are often advised to avoid strenuous activities and driving for at least a week.
But Dr. Smith said it depends on the individual patient and, in particular, whether they have other underlying health problems.
“It depends on how well your heart is pumping,” Dr. Smith said.
“Patients typically return home within 24 hours, usually to begin cardiac rehabilitation.”
As for the patient who took a transatlantic flight, Dr. Smith said that would have to be decided on a case-by-case basis.
“It depends on how they do and the length of the flight,” he said.
- Any reader who thinks they may be having a heart attack, or have had one, should never diagnose themselves. Always call 911 if you think you might be having a heart attack. Your ambulance emergency medical team will direct you to the correct hospital based on your location.