More than half of dogs harbor an antibiotic-resistant superbug that is easily transmitted to humans, a new study has revealed.
A team of Chinese scientists has discovered that most dogs suffering from diarrhea carry multidrug-resistant strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), an intestinal microbe that does not respond to some or all antibiotics.
Humans infected with E. coli can experience diarrhea, stomach cramps, fever, and, in rare cases, kidney failure and death.
The team analyzed stool samples from 135 dogs that had diarrhea and found that more than 50 percent of the canines carried the bacteria.
Drug-resistant superbugs are likely becoming more common due to the widespread use of antibiotics in agriculture and medicine, the scientists behind the new work concluded.
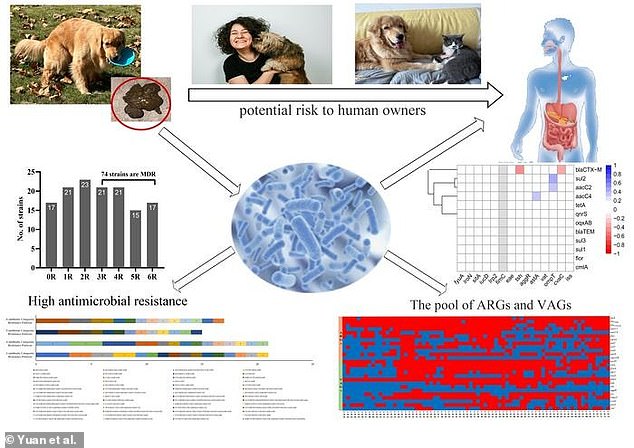
Dogs with diarrhea may be shedding multidrug-resistant E. coli in 5 out of 10 cases, with potential risks to their human owners.


Your pet could be carrying antibiotic-resistant superbugs, bacteria that cannot be treated with conventional antibiotics.
This overwhelming presence of superbugs among companion animals could accelerate the emergence of new drug-resistant diseases in people, the scientists wrote.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), superbugs kill more than a million people every year. The organization has warned that the planet is heading towards a ‘post-antibiotics’ era.
In fact, up to half of multidrug-resistant infections are acquired in hospitalfound a large-scale study.
A post-antibiotic era would effectively turn back time, placing us in an era where a simple surgery or scrape could turn into a life-threatening medical emergency.
And according to the new study, dogs may play a role in the spread of these dangerous bacteria.
The scientists took 185 stool samples from dogs that had confirmed cases of diarrhea over a one-year period.
Dogs that had taken antimicrobial medications of any type in the past three months were excluded to ensure they got a relatively unaltered view of their bacterial content.
The team then extracted and cultured E. coli bacteria from the samples, ending up with 135 that they grew in dishes for further testing.
They then tested 16 different antibiotics, comprising six categories of drugs, on each sample to see which ones were effective.
Between 59 and 76 percent of the samples contained bacteria resistant to an entire class of drugs.
Specifically, 59 percent of the samples were resistant to sulfonamides, 64 percent were resistant to tetracyclines, and 76 percent were resistant to beta-lactams.
These three classes include the most commonly used antibiotics.
“The widespread use of antibiotics has significantly led to an increase in (multidrug-resistant) E. coli isolated from companion animals,” wrote the team from the School of Veterinary Medicine at Sichuan Agricultural University.
Antimicrobial chemicals in everyday items like hand soap have also been linked to increasing rates of drug-resistant bacteria, as has the use of alcohol and bleach to disinfect homes and hospitals.
Part of what makes E. coli resistant to antibiotics is an accelerated form of evolution: survival of the fittest.

E. coli is a type of bacteria that exists naturally in our intestines, as well as those of dogs. But an excessive amount can make us sick and E. coli is increasingly resistant to common treatments.
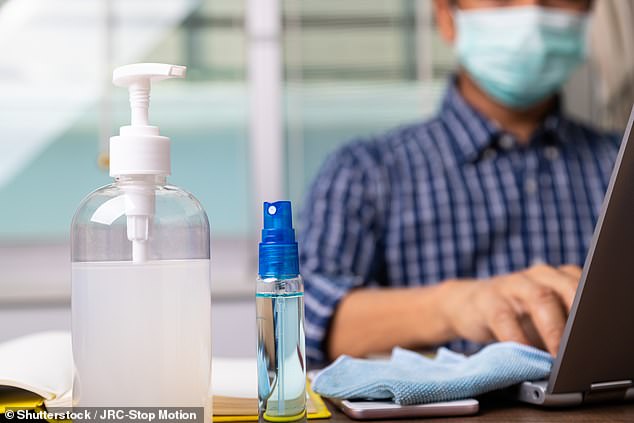


Disinfectants and antiseptics are commonly used to clean surfaces, surgical instruments, and even skin in healthcare environments. But these could increase antibiotic resistance as they leave survivors behind.
When a dog or human is treated with an antibiotic, harmful bacteria are killed.
But it may not be 100 percent of them.
Those that survive are able to survive because they have specific genetic variants that give them protection against antibiotics.
When these bacteria survive, they pass on their resistance genes to their offspring.
Not only that, but bacteria can also share genetic material with each other. That means they can pass resistance genes to each other without even reproducing.
In recent years, restrictions on antibiotic prescribing have tried to improve the situation, but according to the new study, the problem may be too advanced to control.
The high detection rates of E. coli (MDR) in our study implied that more effective measures should be taken to control the emergence and spread of E. coli (MDR) from companion animals,’ the researchers wrote.
