The air pollution women breathe during pregnancy may be linked to an increased risk of developing autism, according to new research.
A more recent literature review found that babies with a genetic predisposition to autism exposed to four common air pollutants were more likely to develop the condition.
It is thought that when breathed during early childhood or in utero, these pollutants can pass into the bloodstream. There, they can bypass the brain’s protective layers, causing inflammation and changing the way nerves function and develop.
Autism rates have increased worldwide over the past few decades. A recent analysis showed that in the US, rates have nearly tripled in children and young adults, and approximately three in every 100 children have autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Dr. Haitham Amal, head of the department of the Laboratory of Neuromatics, Cell Signaling and Translational Medicine at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, said they were trying to understand what could be contributing to this increase in diseases.
His lab has focused primarily on nitric oxide (NO), a gas released when fuel is burned in cars.
Dr. Amal said, “My laboratory has shown that NO plays an important role in ASD.”
This comes as the American Lung Association reports that 39 percent of the U.S. lives in an area with a high amount of air pollution, including some of the chemicals studied in the new paper.
Use the map below to see how the air matches up in your city.
Dr. Amal (center) and his team of researchers in their laboratory in Jerusalem. The team focuses on nitric oxide and its role in the brain.
Some of the cities with the worst air pollution were Phoenix, Arizona, San Jose, California, and Eugene, Oregon. Organizations like the EPA are tracking these contaminating chemicals and reporting them so you can get an idea of your risk.
In the new study, published in the magazine Brain medicineDr. Amal’s team reviewed studies that looked at children with autism, studies that used human cells, and studies that used mice.
They studied four different components of air pollution: particles, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and ozone.
Particles, which are microscopic pieces of dust, liquid, or smoke produced at construction sites, power plants, and automobiles.
It is between seven and 30 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair.
Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas or liquid and is produced when fossil fuels are burned or when metal such as aluminum is melted, according to Wisconsin. Department of Health Services.
Ozone is a colorless, odorless gas produced in chemical plants, oil-based paints and printing presses, according to the EPA.
They found that people with a genetic predisposition to autism who were exposed to air pollution early in life were more likely to develop the condition than people exposed to less air pollution.
The authors did not provide a figure, but older Harvard research found that exposure to air pollution, such as particulate matter, can increase the risk of ASD by up to 64 percent.
Doctors aren’t sure what causes the condition, but about 15 percent of autism cases are linked to a specific genetic mutation. Other people may be more likely to develop autism if someone in their immediate family has the condition.
They’re not sure why they might be linked, but they have some theories.
First, when someone inhales one of these pollutants, it can cause inflammation in the nerves, which damages them over time and leads to dysfunction.
People are most vulnerable to these effects when they develop in utero and early childhood, because their brains are still forming, Dr. Amal said.
Studies have shown that these small polluting particles can even directly enter the brain of the fetus, he said.
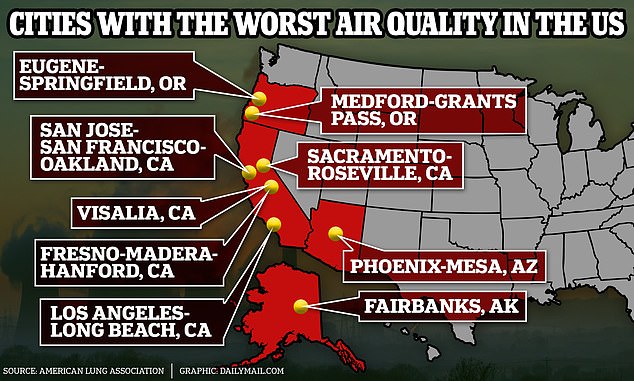
The American Lung Association ranked the top cities suffering from the worst air quality in the U.S., affecting approximately 131 million Americans.
Long-term changes in the way the brain works can cause some of the behavioral symptoms associated with autism, he said.
According to the NIH, ASD is a developmental disorder that affects the way people interact with others, communicate, learn, and behave.
It could also be causing a higher incidence of autism because ingesting polluted air can disrupt the production of some chemicals that govern the brain, including dopamine and norepinephrine.
These chemicals are crucial in the decision-making process and in brain development in general.
Whatever the cause, Dr. Amal said he is proud of his research team, which is one of the first to link these air pollutants to the autism spectrum.
When asked what his greatest achievement was, Dr. Amal said, “discovering that nitric oxide plays a key role in autism.”


