It’s a familiar situation: You spend every morning at the gym and resist sweets, but you still can’t get rid of those extra pounds.
There’s a growing body of research suggesting that you may be making a crucial mistake, one that can easily be corrected by using your fitness tracker.
Fitness experts say that a key way to optimize calorie burn is to make sure you hit a specific heart rate range while exercising.
This fat burning window varies depending on multiple factors including age, stress levels, medication you are taking, and how much coffee you have drunk.
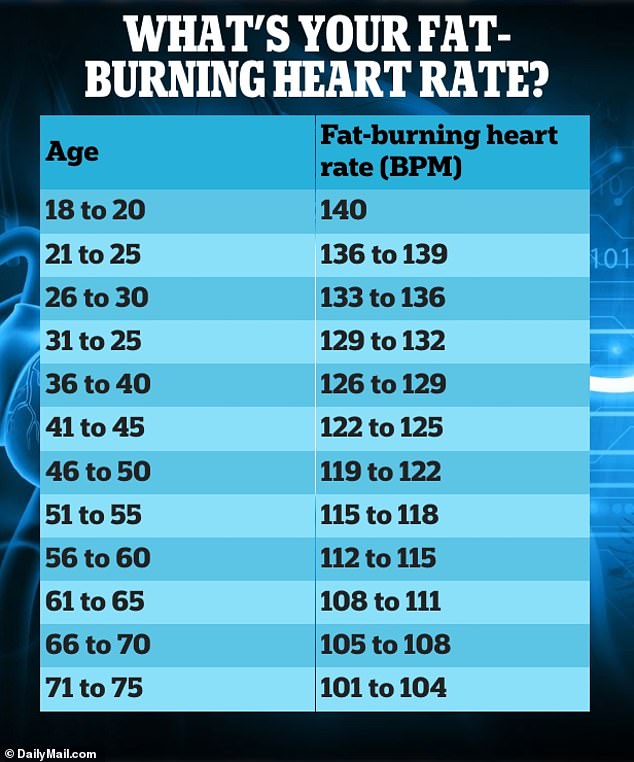
Below, a table from DailyMail.com reveals the range you should hit in your next workout to lose weight faster.

There is growing evidence that your heart rate plays a key role in the productivity of your workout and the likelihood that you will burn more calories.
The ideal average resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute, although several factors can cause it to increase, including exercise.
Maximum heart rate is the greatest number of times a person’s heart can beat per minute without causing stress to the organ.
This depends on age and tends to decrease over time.
The main way to determine your maximum heart rate is to subtract your age from 220. For example, a 50-year-old person would have a maximum heart rate of 170.
Exercise consumes energy; more intense exercise burns more energy and increases heart rate.
As the intensity increases, the body must use fat stores for energy instead of sugars and carbohydrates. Doing this consistently helps burn fat and leads to weight loss.
This is known as your fat-burning heart rate, which is about 70 percent of your maximum heart rate.
So, that same 50-year-old would want to keep their intensity at around 119 beats per minute while exercising to burn fat.
Similar to maximum heart rate, fat-burning heart rate decreases with age.
Thus, while an 18-year-old would need to stay around 140 beats per minute, a 75-year-old would only need to reach 101 beats per minute.
However, certain medications can increase or decrease heart rate. Beta blockers, for example, reduce heart rate by blocking the effects of hormones such as adrenaline.
They are usually prescribed for unexplained tachycardia (resting heart rate greater than 100 bpm) and high blood pressure.
Additionally, some over-the-counter antibiotics, corticosteroids, and decongestants can increase heart rate.
To avoid putting too much stress on your heart, it is essential to consult a doctor about the ideal heart rate to aim for if you are taking any of these medications.
If you want to make sure you stay in the fat-burning zone, there are several ways to monitor your heart rate.
The traditional method involves using your fingers to follow the pulse on your neck, wrist, or chest.
However, wrist-worn monitors like the Apple Watch are much more common and can track heart rate throughout an entire workout and during rest.
According to the federal Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, adults need about 150 minutes of moderate physical activity each week or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise.
The Department of Health and Human Services also suggests that American adults do at least two days of muscle-strengthening exercise, such as weight lifting, each week.
| Age | Fat Burning Heart Rate (BPM) |
|---|---|
| 18 to 20 | 140 |
| 21 to 25 | 136 to 139 |
| 26 to 30 | 133 to 136 |
| 31 to 35 | 129 to 132 |
| 36 to 40 | 126 to 129 |
| 41 to 45 | 122 to 125 |
| 46 to 50 | 119 to 122 |
| 51 to 55 | 115 to 118 |
| 56 to 60 | 112 to 115 |
| 61 to 65 | 108 to 111 |
| 66 to 70 | 105 to 108 |
| 71 to 75 | 101 to 104 |